A phobia is an irrational fear of something that’s unlikely to cause harm. The word itself comes from the Greek word phobos, which means fear or horror.
People with phobias actively avoid the phobic object or situation, or endure it within intense fear or anxiety.
Phobias are a type of anxiety disorder. Anxiety disorders are very common. They’re estimated to affect more than 30 percent of U.S. adults at some time in their lives.
Arachnophobia
Arachnophobia, otherwise known as spider phobia, is the intense fear of spiders and other arachnids. Classified as a specific phobia, arachnophobia causes clinically significant distress that can impact an individual's quality of life. When in contact with, or thinking about arachnids, individuals will likely feel fear and experience symptoms of anxiety almost immediately.
Symptoms
- Immediate fear and anxiety when you see or think about a spider
- Fear or anxiety that is out of proportion to the danger the spider poses to you
- Avoidance of spiders
- Panic and/or anxiety responses, such as difficulty breathing, rapid heart beat, nausea, sweating, trembling, and a need to escape
Causes
Arachnophobia may be caused by experiencing one or multiple traumatic encounters with spiders. Arachnophobia may also be caused by:
- An evolutionary response: Research suggests that arachnophobia or a general aversion to spiders is hard-wired as an ancestral survival technique.
- Cultural and/or religious beliefs: Some individuals within certain cultural or religious groups seem to have phobias that stem from these influences. These particular phobias differ from phobias that are common in the general population, making culture and religion potential factors in phobia development.
- Genetic or family influences: Researchers believe that there may be a genetic component linked to phobias. Family environmental factors may also influence the development of phobias. For example, if a parent has a specific phobia to something, a child may pick up on that fear and develop a phobic response to it.
Treatment
- Cognitive reframing: This method helps you shift the way you look at something so you no longer perceive it as dangerous or stressful. This may eventually change your physical reaction to a triggering stimulus, such as seeing a spider.
- Systematic desensitization: In this method, you employ relaxation techniques and then confront your fears from the least fear-producing to the most.
Another type of Phobias
-Astraphobia, fear of thunder and lightning

-Autophobia, fear of being alone

-Claustrophobia, fear of confined or crowded spaces

-Hemophobia, fear of blood
-Hydrophobia, fear of water
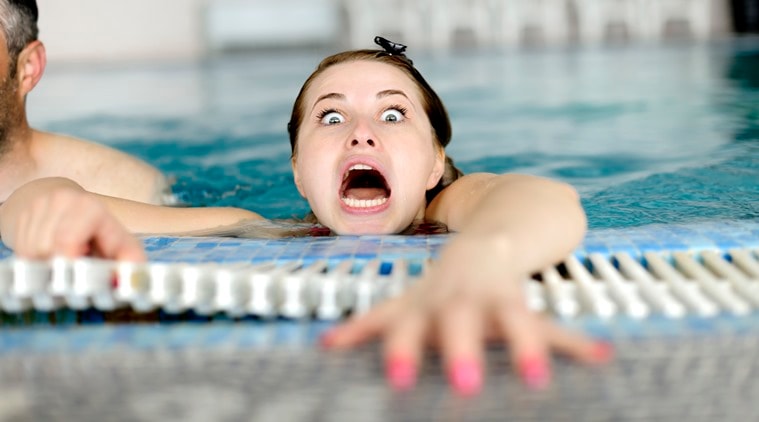

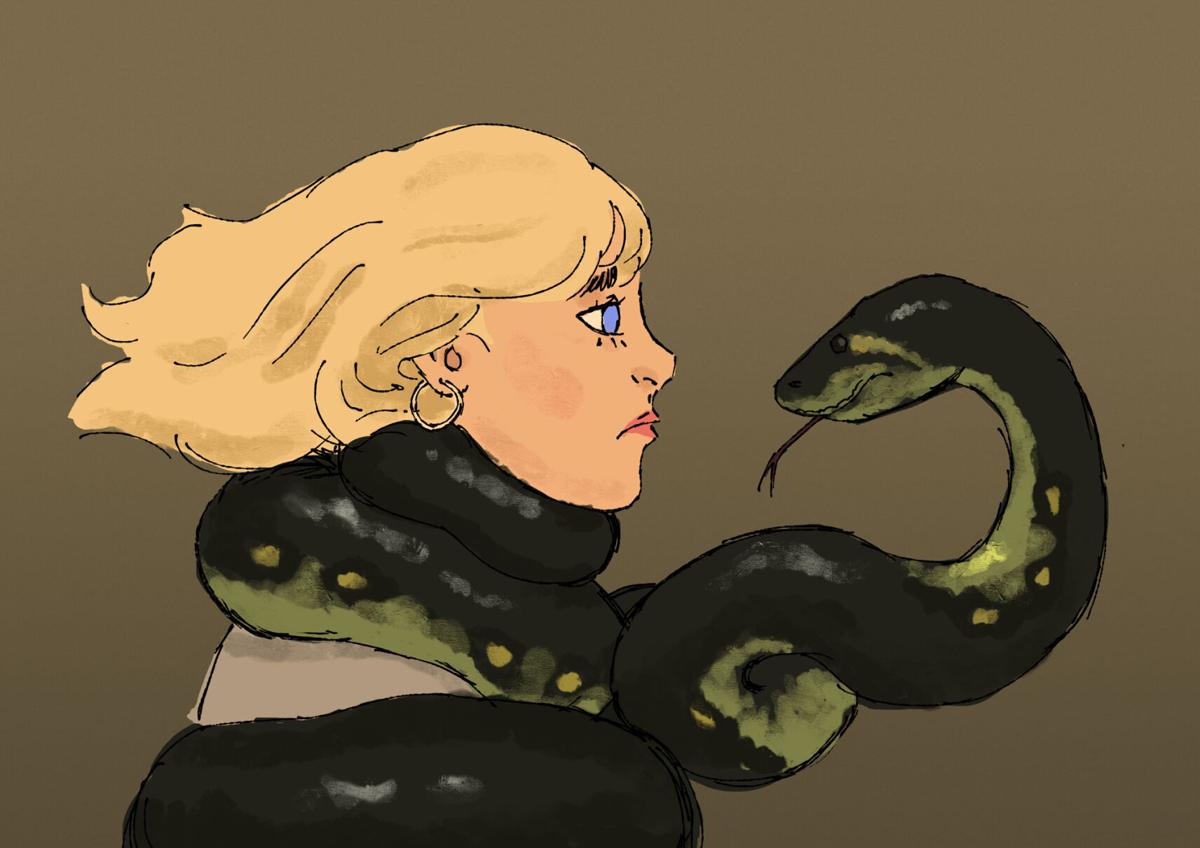
-Ophidiophobia, fear of snakes


-Autophobia, fear of being alone

-Claustrophobia, fear of confined or crowded spaces

-Hemophobia, fear of blood

-Hydrophobia, fear of water

-Ophidiophobia, fear of snakes

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-510827251web-56df2d7f3df78c5ba054c774.jpg)
